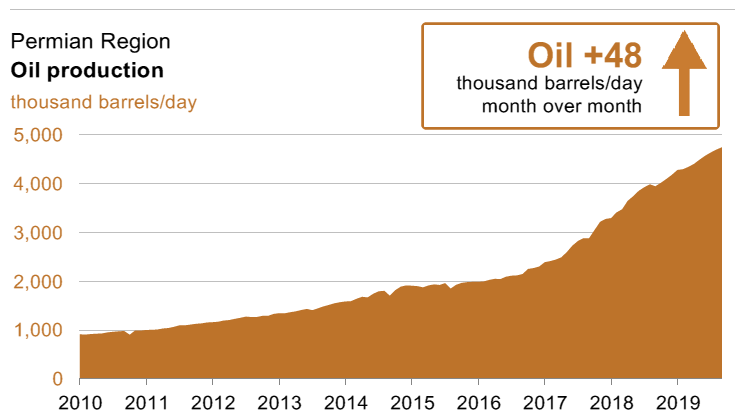
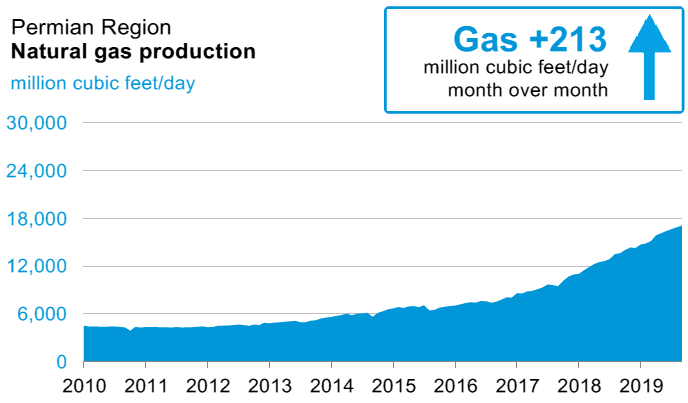
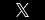Landowners are often faced with a conundrum: can they accept a royalty check if they believe it is in the wrong amount?
Ms. Strickhausen owns a half interest in the minerals under a tract of land in La Salle County. Her minerals are subject to a lease owned by BPX (then Petrohawk, subsequently acquired by BPX). Her lease expressly prohibits pooling without her consent. The lease of the other half interest in her tract permits pooling. (Ms. Strickhausen’s lease also prohibits commingling of production: “Commingling of production from the Leased Premises with production from other lands or leases shall be prohibited prrior to such accurate metering, measuring and testing, unless commingling is consented to, in writing, by Lessor and each royalty owner.”) BPX filed a pooled unit designation for the WK Unit 4 No. 1H Well and drilled a horizontal well located partly under Ms. Strickhausen’s tract and partly under other tracts. It then asked Ms. Strickhausen to ratify the pooled unit.
Ms. Strickhausen’s lawyer then engaged in a series of communications with BPX seeking to negotiate terms under which Ms. Strickhausen would agree to ratify the pooled unit. The attorney asked BPX how it would propose to pay Ms. Strickhausen if she refused to ratify the unit. BPX replied that it would pay her “based on the length of productive wellbore on the subject tract over the total length of productive wellbore.” BPX claimed that Ms. Strickhausen would receive a larger royalty interest in the well by ratifying the pooled unit than she would if she were paid on a productive-wellbore basis. BPX concluded by saying that, if Ms. Strickausen did not ratify the unit “the royalties will require being placed in suspense.” Continue reading →
 Oil and Gas Lawyer Blog
Oil and Gas Lawyer Blog