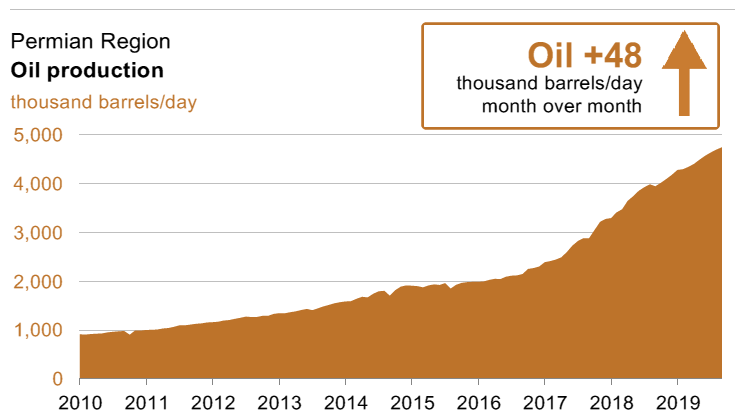
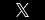Here’s a novel idea: use gas that would otherwise be flared to generate electricity in the field and use it to mine bitcoin. Believe it or not, it is being done. In North Dakota, Equinor and Enerplus are among the operators using the process. New companies like Crusoe Energy have sprung up to provide the in-the-field equipment. Crusoe has some 40 mobile generating units in oil shale basins and plans on increasing that number to 100. A recent conference in Houston on the subject saw 200 oil and gas execs and bitcoin miners in attendance.
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency or digital currency, created in 2009. There is no physical coin, only a balance kept on a public ledger. It can be used to purchase goods and services, for those companies that accept bitcoin as payment. Mostly, bitcoin are bought and sold as a type of investment. As of this writing, one bitcoin sells for $47,706.80. Bitcoins are not backed by any hard asset or any government.
So what is “mining” bitcoin? See explanation here. “Bitcoin mining is performed by high-powered computers that solve complex computational math problems; these problems are so complex that they cannot be solved by hand and are complicated enough to tax even incredibly powerful computers.” One with a computer that solves the problem is given a “block reward,” currently 6.25 bitcoins. The amount of electricity being used to run computers mining bitcoin is enormous; the global bitcoin industry’s consumption of electricity is causing emissions of 60 million tons/year of CO2. That’s the equivalent of about nine million cars.
 Oil and Gas Lawyer Blog
Oil and Gas Lawyer Blog