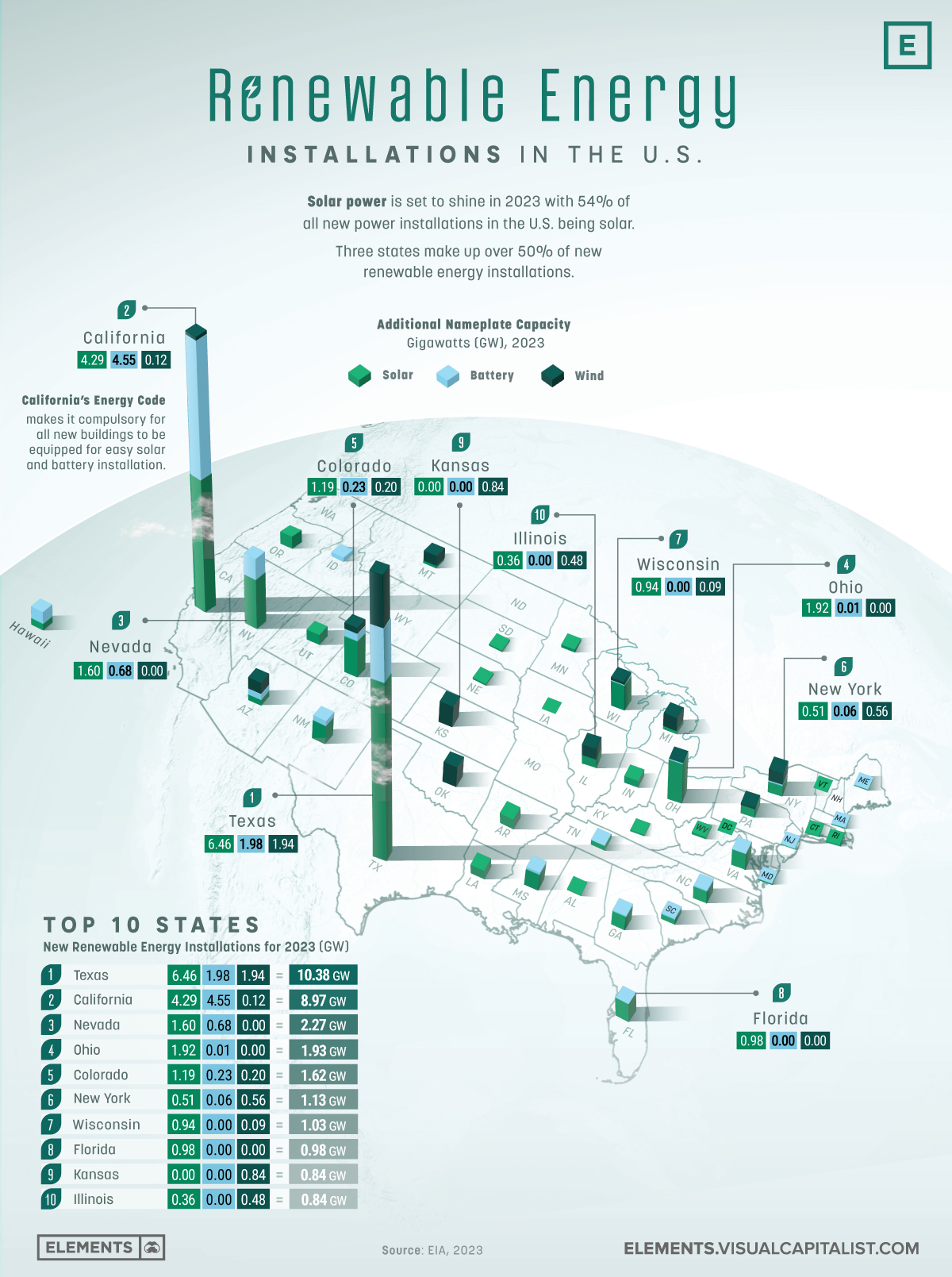
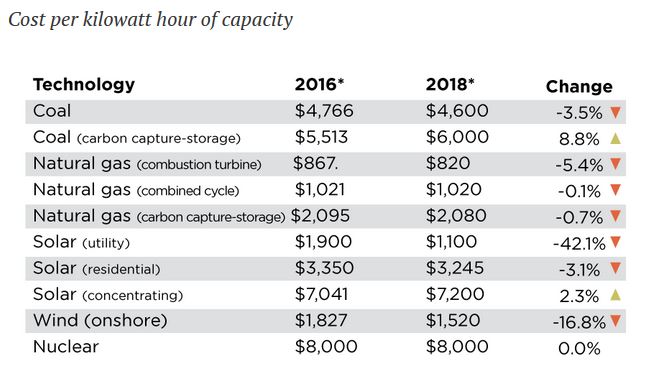
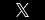From Visual Capitalist (click on image to enlarge):
Articles Posted in Alternative Energy
New Industry Group Forms to Promote Texas Geothermal Energy
A friend alerted me to a new organization formed to promote geothermal energy, The Texas Geothermal Energy Alliance (TxGEA). TxGEA is an interdisciplinary group of entities engaged in geothermal resource exploration, drilling, construction and production, for producing electricity from geothermal resources. Membership includes:
- Baker Hughes
- Blade Energy Partners
Excellent Report from Deloitte on Transitioning to Renewable Energy Sources
A recent report from Deloitte provides a good perspective on the prospects for wind and solar electricity.
Some takeaways:
Costs of wind and solar are now competitive with coal and gas. “Power purchase agreement (PPA) prices for wind and solar power are also competitive with other resources. The weighted average US price for the first half of 2021 from auction and PPAs for solar PV is US$31/MWh, while for onshore wind it is US$37/MWh. This compares to a weighted average wholesale electricity price of about US$34/MWh across US markets during the same period.” It now costs less to build new solar and wind plants than to continue operating existing coal-fired plants. Wind and solar costs are projected to fall by half by 2030.
Two Developments in Efforts to Stem Climate Change
Two recent articles caught my eye:
“The world’s biggest plant to capture CO2 from the air just opened in Iceland,” from the Washington Post.
“Utilities eye mini nuclear reactors as climate concerns grow,” from the Wall Street Journal.
Solar Energy in Texas and the Chadbourne Ranch
The Texas Observer has a great article about Texas solar energy development, Texas Solar Hits a Turning Point, by Nancy Nusser. The article focuses on a new solar farm on the Chadbourne Ranch in Nolan County, owned by Garland Richards. The Holstein solar farm has 709,000 solar panels on 1,300 acres and can generate 200 megawatts of electricity, enough to power about 40,000 homes.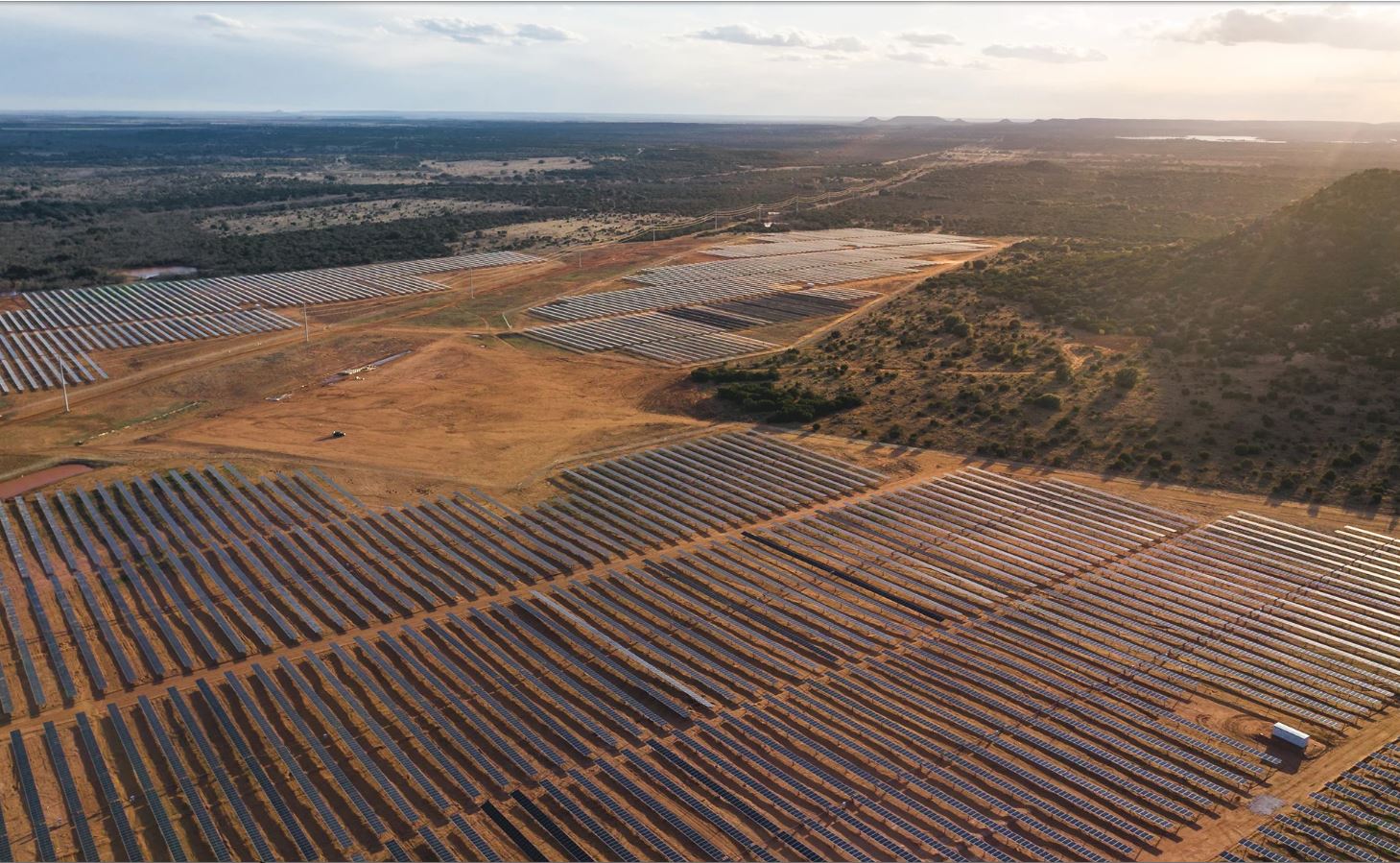
According to the article there are now 17 solar facilities in Texas, 13 of which can produce at least 100 megawatts. And more coming. Solar capacity in the ERCOT service area is expected to increase 150 percent this year to 5,777 megawatts, and next year to 13,449 megawatts. Still, solar provides only about 2 percent of Texas’ electricity generation. If 1,300 acres of solar farm generates 200 megawatts, and if Texas needs 300,000 megawatts of electricity, and if solar were to provide 20% of that, it would take 300 solar farms like the one above to provide that power, or almost 400,000 acres of solar farms – 600 square miles.
 Chadbourne Ranch is the site of Fort Chadbourne, established by the army in 1852 in what is now Coke County, to protect the western frontier. The fort surrendered to confederates on February 28, 1861, before the confederate shelling of Fort Sumter on April 12 of the same year. It was reoccupied by federal troops from 1865 to 1867, and is on the National Register of Historic Places. Garland Richards helped form the Fort Chadbourne Foundation, which has preserved the fort, reconstructed some buildings, and built a museum housing artifacts discovered during restoration of the site. Restored barracks below.
Chadbourne Ranch is the site of Fort Chadbourne, established by the army in 1852 in what is now Coke County, to protect the western frontier. The fort surrendered to confederates on February 28, 1861, before the confederate shelling of Fort Sumter on April 12 of the same year. It was reoccupied by federal troops from 1865 to 1867, and is on the National Register of Historic Places. Garland Richards helped form the Fort Chadbourne Foundation, which has preserved the fort, reconstructed some buildings, and built a museum housing artifacts discovered during restoration of the site. Restored barracks below.
The Future of Alternative Energy
I attended the Symposium of the Texas Journal of Oil, Gas and Energy Law at UT last week. One of the speakers was Giji M. John, Partner at Orrik, Houston, on renewable energy. Here are some takeaways. (click on images to enlarge.)
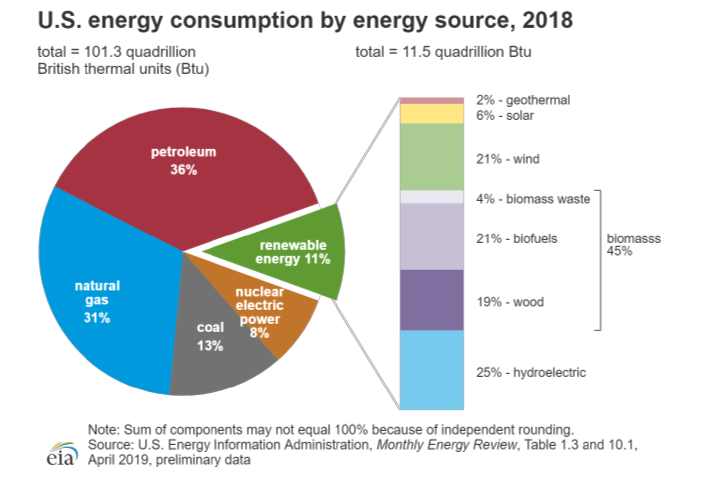
Renewable energy’s contribution to US energy consumption in 2018 was 11%. Of that 11%, wind energy contributed 21% and solar 6%. Remarkably, “wood” was 19% of that 11%. So solar and wind combined contributed 27% of 11%, or less than 3%, of energy consumed in the US.
 Texas is by far the leader in wind energy production, with 24,895 megawatts of installed capacity. The next state is California with 5,840 MW.
Texas is by far the leader in wind energy production, with 24,895 megawatts of installed capacity. The next state is California with 5,840 MW.
Lyle v. Midway Solar – Solar Farm Meets Accommodation Doctrine
Plaintiffs Kenneth Lyle and Linda Morrison have appealed the dismissal of their suit against Midway Solar to the El Paso Court of Appeals, No. 08-19-00216-CV. Lyle and Morrison own the minerals under 315 acres in Pecos County. Midway Solar has constructed a solar farm on 215 of those acres.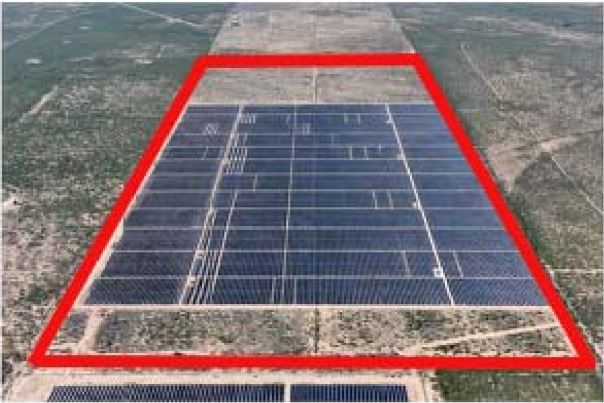 
 Typically, a solar developer will obtain surface-use waivers from mineral owners before building a facility. Midway did not do that. Instead, it set aside portions of the 315 acres, on the north and south ends of the property, to allow for development of the minerals by directional drilling.
Typically, a solar developer will obtain surface-use waivers from mineral owners before building a facility. Midway did not do that. Instead, it set aside portions of the 315 acres, on the north and south ends of the property, to allow for development of the minerals by directional drilling.
Lyle and Morrison contend their minerals are not susceptible to development by directional or horizontal drilling, because of the subsurface geology. They say 70% of their tract cannot be developed for minerals. Their minerals are not now leased and there are no plans to drill wells. There has been production from wells in the vicinity.
The cost of electricity
From an article in the Dallas Morning News, “Texas power costs: What’s the cheapest way to generate electricity?”
Pecos County is Center of Solar Power Boom
174 Power Global Corp., a subsidiary of South Korea’s Hanwha Energy, held its groundbreaking last week for the largest solar power project in Texas: a 236-MW plant to be built in Pecos County. It will sell its power – enough to power more than 50,000 homes – to Austin Energy, Austin’s municipally owned power provider.
Other Texas solar projects:
NRG’s Buckthorn Solar Farm, 200 MW in Pecos County, to supply the City of Georgetown, the largest municipality in the country powered solely by renewable sources.
The Rise of Solar Power
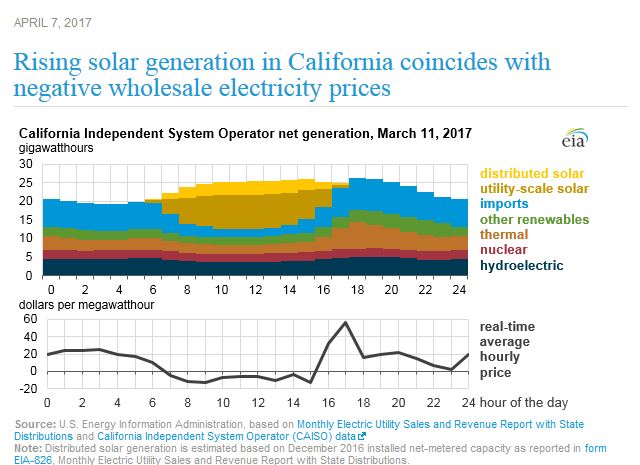
For a few hours on March 11, for the first time, more than half the electric power used in California came from solar power, according to the US Energy Information Administration. The wholesale price for electricity went negative. In other words, power generators had to pay wholesalers to take their electricity. Conventional power generators would prefer to pay customers to take their power rather than shut down their plants. Germany, with lots of solar and wind generation, sometimes has to pay neighboring countries to take its electricity. Lack of a viable way to store electricity still presents an obstacle for transition to renewable power sources, but clearly wind and solar have come to stay.
Solar farms are under development or in various stages of construction in West Texas, able to hook into the new transmission lines constructed originally to bring wind power from North and West Texas. A facility in Pecos County that went on line April 5 covers about 1,000 acres with 1.2 million solar panels, and took about a year to construct. Austin’s municipally owned utility Austin Energy has contracted to buy all of its output, which is capable of supplying enough electricity to serve the equivalent of 24,000 homes in the summer and 40,000 to 50,000 homes in the winter. Austin Energy aims to obtain 55 percent of its electricity from renewable energy sources and now is at 30 percent.
In Plano, Texas, a solar system is being installed at Toyoto’s new headquarters, atop four parking garages. It will consist of 20,000 solar panels covering the equivalent of ten football fields and shading the cars beneath.
 Oil and Gas Lawyer Blog
Oil and Gas Lawyer Blog